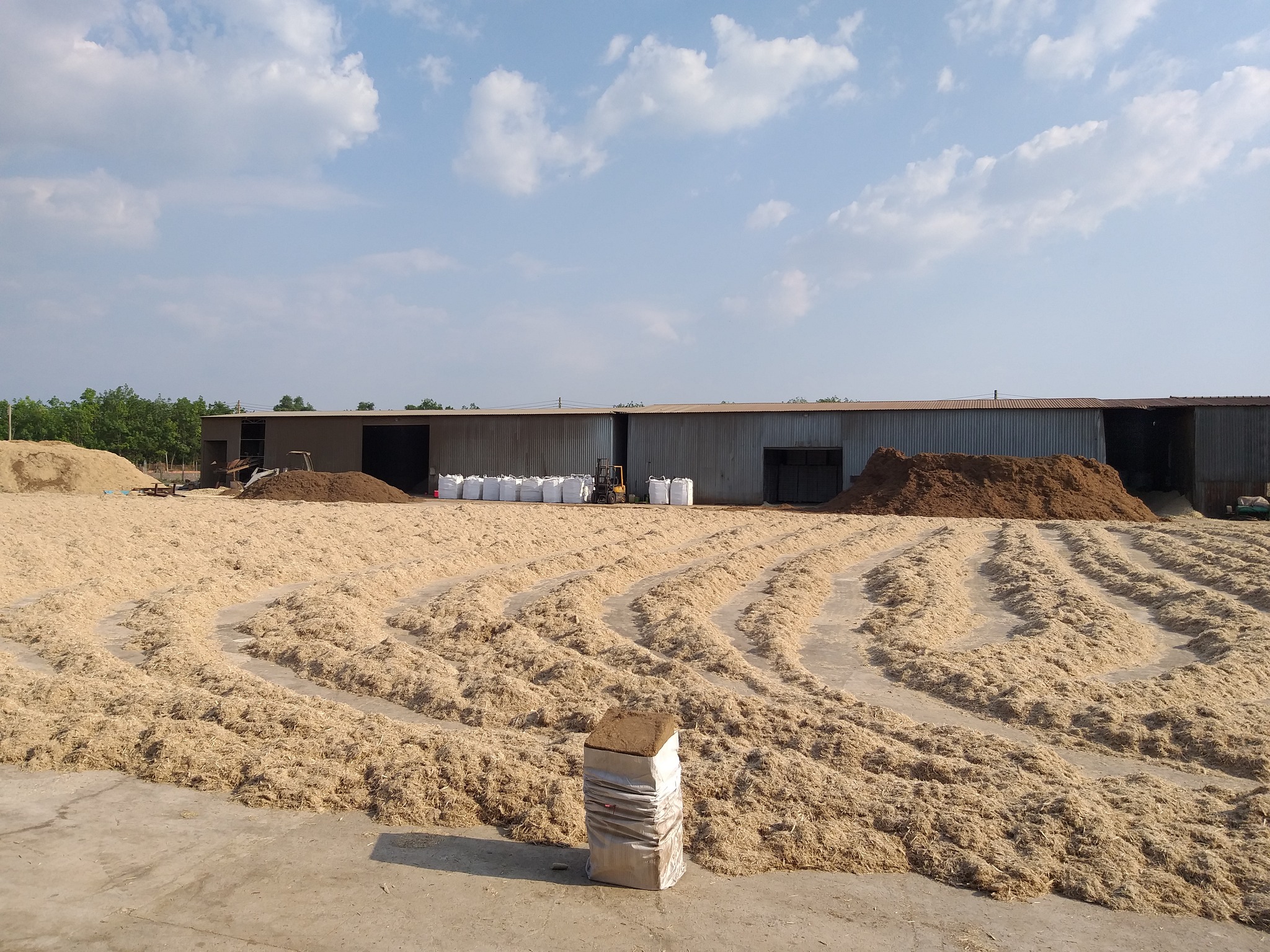
Bagasse, the fibrous residue left behind after extracting juice from sugarcane, emerges as a sustainable and versatile resource with transformative potential across various industries. Often overlooked as waste, bagasse embodies a wealth of untapped opportunities, from eco-friendly packaging solutions to renewable energy production, underscoring its pivotal role in driving sustainability initiatives worldwide.

Originating from the fibrous stalks of sugarcane, bagasse undergoes a process of extraction and refinement during sugar production, resulting in the separation of juice and fibrous residue. Once considered a byproduct destined for disposal, bagasse has now emerged as a valuable resource, offering a myriad of eco-conscious applications that mitigate environmental impact and promote circular economy practices.
In the realm of packaging, bagasse stands as a beacon of sustainability, offering a renewable alternative to conventional materials like plastic and styrofoam. By harnessing its natural strength and biodegradability, bagasse-based packaging solutions provide a guilt-free option for consumers and businesses alike, reducing dependence on finite resources and minimizing plastic pollution in landfills and oceans.
Moreover, bagasse finds utility in the production of paper and pulp products, serving as a primary raw material for manufacturing biodegradable plates, bowls, cups, and packaging trays. Its fibrous composition and absorbent properties make it an ideal substrate for papermaking, yielding high-quality products that meet rigorous standards of sustainability and performance.
Beyond its applications in packaging and paper products, bagasse plays a pivotal role in renewable energy production, contributing to the generation of biofuels and green electricity. Through processes like anaerobic digestion and biomass combustion, bagasse can be converted into biogas, bioethanol, and electricity, providing clean and renewable energy sources that reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.

Furthermore, bagasse serves as a valuable resource in agriculture and horticulture, where it finds utility as a soil amendment and livestock feed. When used as compost or mulch, bagasse enriches soil fertility, promotes moisture retention, and enhances crop productivity, contributing to sustainable farming practices and soil conservation efforts.
In essence, bagasse embodies the principles of sustainability, innovation, and resourcefulness, offering a holistic solution to environmental challenges while fostering economic growth and social responsibility. As industries increasingly embrace the circular economy model and prioritize sustainability in their operations, bagasse emerges as a shining example of nature’s ingenuity and humanity’s potential to create positive change for generations to come.
Related products
-10%
Coconut Products
-28%
Pets Products