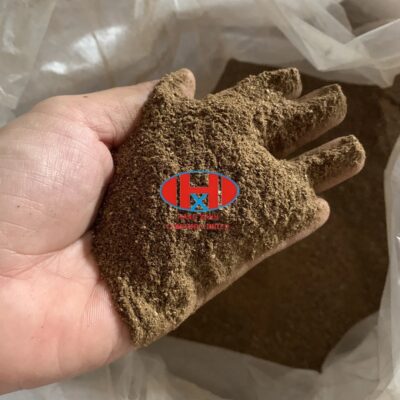
Beer meal residue, often overlooked in the brewing process, emerges as a valuable co-product with diverse applications ranging from animal feed to sustainable agriculture. Originating from the spent grains left behind after brewing beer, this residue embodies a wealth of nutrients and functional properties, transforming waste into a valuable resource in various industries.


During the brewing process, grains such as barley, wheat, and rye are steeped in hot water to extract fermentable sugars, enzymes, and flavors, creating the wort used to produce beer. Once the sugars are extracted, the spent grains, known as beer meal residue, remain as a byproduct.
Despite being considered waste by brewers, beer meal residue holds significant nutritional value and functional benefits. Rich in protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, it serves as a nutritious feed supplement for livestock, providing essential nutrients for growth and health. As a sustainable alternative to conventional feed ingredients, beer meal residue helps reduce reliance on soybean meal and other imported feeds, contributing to local agriculture and food security.
Furthermore, beer meal residue finds utility in sustainable agriculture practices, where it serves as a soil amendment and organic fertilizer. Its high organic matter content improves soil structure, enhances moisture retention, and promotes microbial activity, leading to healthier soils and increased crop yields. By returning organic nutrients to the soil, beer meal residue closes the loop in the agricultural cycle, fostering regenerative practices that benefit both the environment and farming communities.
In addition to its agricultural applications, beer meal residue holds promise in bioenergy production and biorefinery processes. Through technologies like anaerobic digestion and biomass conversion, it can be transformed into biogas, biofuels, and biochemicals, offering renewable energy sources and sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels.
Moreover, beer meal residue serves as a symbol of circular economy principles, where waste is repurposed and transformed into valuable resources. By harnessing the potential of this co-product, breweries can minimize waste generation, reduce environmental impact, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
In summary, beer meal residue represents a paradigm shift in waste management and resource utilization, where what was once considered waste becomes a valuable asset in multiple industries. From nourishing livestock and enriching soils to powering renewable energy systems, its versatility and sustainability pave the way for a more circular and resilient economy.