Price: Contact
SPECIFICATION
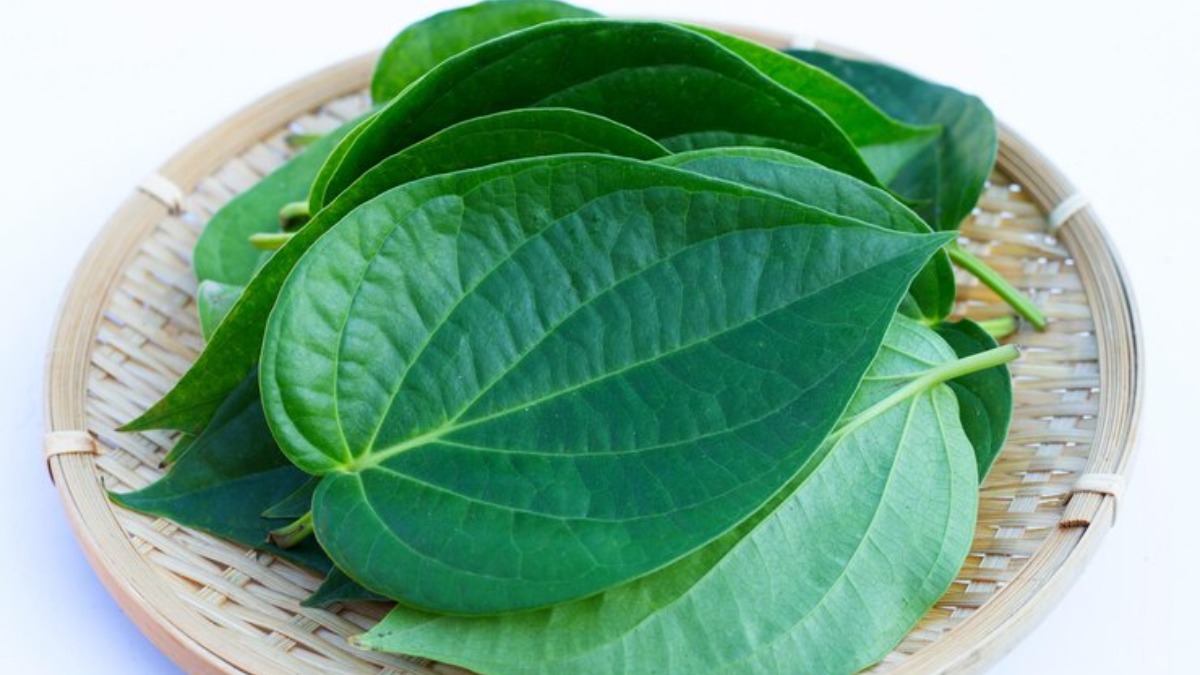
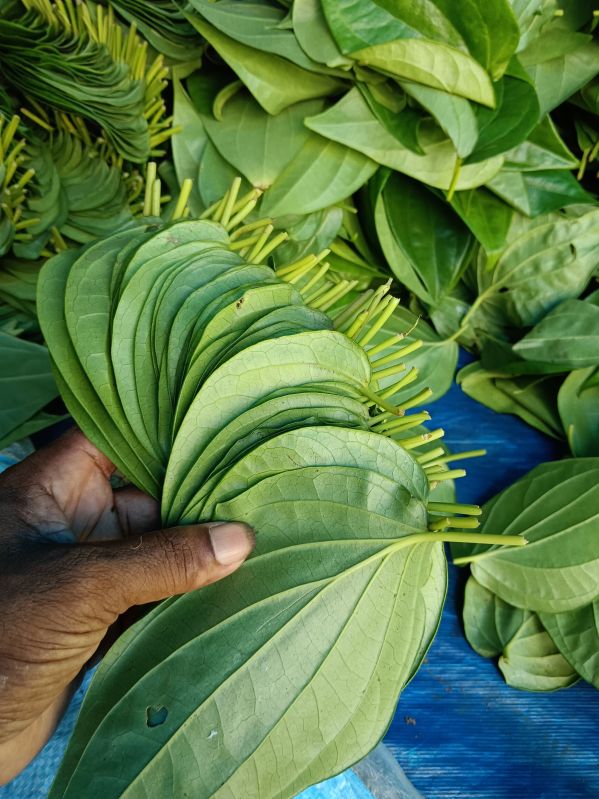
• Botanical Name: Piper betel
• Plant Part: Leaves
• Style: Fresh
• Type: Betel Leaf
• Length: 3 – 6 cm
• Color: Dark Green
• Drying Process: Natural
• Size: Big Leaf 100 pcs Per Kgs
• Storage: Store in dry, cool place away from direct sunlight
PACKING
• Packing: 5kg – 8kg Carton Box or As buyer’s request