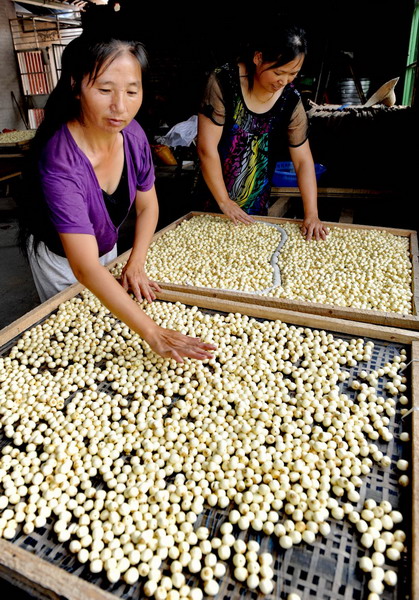
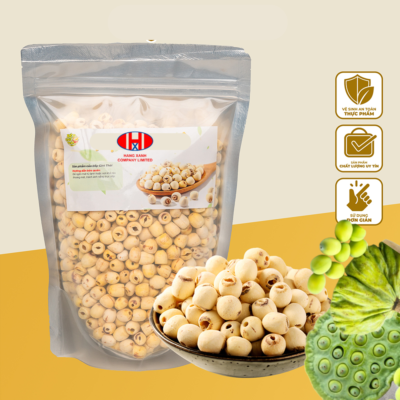
White lotus seeds, known for their symbolic significance and nutritional benefits, are revered in various cultures for their medicinal properties and culinary uses. These seeds come from the white lotus plant (Nelumbo nucifera), a sacred flower often associated with purity and enlightenment.

In traditional medicine, white lotus seeds are valued for their ability to nourish the body and promote overall health. They are rich in essential nutrients such as protein, vitamins (like vitamin B and C), and minerals (including magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus). These nutrients contribute to boosting immunity, improving digestion, and supporting cardiovascular health. Additionally, the seeds are known for their calming properties, aiding in stress reduction and promoting restful sleep.
Culinarily, white lotus seeds are a versatile ingredient used in both sweet and savory dishes across Asia. They can be added to soups, congee, desserts, and teas, imparting a subtle nutty flavor and a pleasant texture. In Chinese cuisine, they are often included in traditional desserts like lotus seed paste-filled pastries and sweet soups.
Beyond their nutritional and culinary uses, white lotus seeds hold cultural significance in many Asian societies, symbolizing purity, fertility, and spiritual enlightenment. They are commonly used in rituals, ceremonies, and religious offerings.
In summary, white lotus seeds are not only a nutritious superfood but also a culturally significant ingredient that has been cherished for centuries for its health benefits and symbolic meanings. Whether consumed for health reasons or integrated into cultural practices, white lotus seeds continue to hold a special place in both traditional medicine and culinary traditions worldwide.